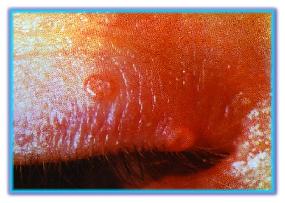
| Molluscum contagiosum is
a disease of the eyelids caused by the molluscum is often
seen in chilldren; in young adult, it can be spread by
sexual transmission. Usually
a single lesion appears, begginning as a papule and
enlarging to a waxy nodule with ann umbilicated center.
Immunosuppressed individuals, such as those with AIDS,
can develop multiple lesions of the eyelid margins and,
rarely, of the conjunctiva.
Patients often present
with follicular conjunctivitis, with or without punctate
epithelial keratitis, subepithelial infiltrates, and
vascular pannus. Preauricular lymphadenopathy can be
present. Some patients with chronic conjunctivitis may
fail to notice a small molluscum contagiosum nodule
hidden within the eyelashes.
This infection is usually
self-limited, but it can persist for 2 years of more.
When it is persistent or when it is complicated by
symptomatic keratoconjuctivitis, excision, incision, or
cryotherapy of the lesion may be considered.
|
 |

