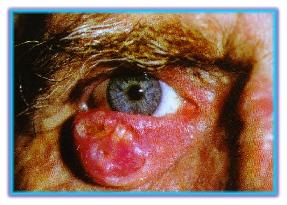
| Like basal cell
carcinoma, most squamous develop in fair-skinned
individuals over the age of 50. Squamous cell carcinoma is a keratinized
lesion, often affecting the eyelid magin. it can
eventually exent into the orbit or spread via the
regional lymph nodes. the risk of matastases is related
to tumorsize, depth of tumor invasion and degree of
celluar differentiation.if a biopsy confirms the
diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma,surgical excision is
performed with microscopic monitoring of tissuse margin
and eyelid reconstruction.
Two other lesion that may
be mistaken for squamous cell carcinoma are actinic
keratiosis and carcinoma-in-situ of the skin. Actinic
keratoses are usually, but not always, Premalignant
lesion that should have excisional biopsy. These flat,
scaly plaques have an erythematous basee and can be
confused with frank squamous cell carcinoma but are
preinvasive lesions.
Carcinoma-in-situ of the
skin, sometimes called Bowen's disease, is an isolated,
slightly elevated erythematous lesion with
well-demarcated borders. Squamous carcinoma-in-situ is an
intraepithelial lesion that has not invaded basement
membrane, the lesion is then defined as squamous cell
carcinoma.
|
 |

